
Agile Methodology, Customer Experience, DevOps, Nearshore, Product Development, Project Management, Successful Outsourcing
Rotating team members on agile software development teams is a controversial subject. Some leaders in the agile community are strongly opposed to the idea and won’t consider it at any level. Others are open to the subject, but frankly too concerned about the possible downsides to actively plan rotations or even hint to their customers it might be a good idea. And of course, there are the wild-eyed optimists who claim it is the best idea possible for every situation.
Our focus for this article is dedicated teams – teams with members selected for their skills and reliability over the long run. Typically, dedicated teams have no set sunset. They are dedicated to a product or part of a product suite and they generally stay through the active development and maintenance of a product lifecycle – which for enterprise software maybe years. But, that said, the ideas that bring up the subject of rotating members of a dedicated team could apply to any long term project, especially with smaller (3-5 member) teams.
And let’s be honest about one other thing too: the longer the project or product lifecycle, the more likely it is there will be an «unplanned» member rotation. Births, deaths, illness, vacations, career advancements and changes – all sorts of life events have to be managed as a part of maintaining a dedicated team. Even if the time a member is away is relatively short, in less than two weeks, the impact on the productivity of a small team needs to be managed to continue to meet client schedules and expectations. In some cases, the remaining team members can sustain production for a period of time by adding additional hours daily and on weekends, but eventually, that will take a toll on their personal commitment to the team. And when there is an unplanned need to bring in a replacement, there are consequences to the team regardless of the additional manpower provided. In fact, it is well understood that if for some reason two members of a small team needed to be replaced over a short period of time, it would be catastrophic for the team. Bringing the new member «up-to-speed» with mentoring and knowledge transfer takes time and effort of other team members away from their work. And, there is the well-understood impact of a team «forming, storming, norming, and performing» cycles as described by Tuckman. Changing a member of a small team always creates issues. Without some planning and forethought – it can kill the effectiveness of a team for an extended period of time.
So – why would anyone want to consider the idea of rotating team members on dedicated agile teams?
- If unplanned changes in a dedicated team are going to happen anyway, why not be prepared? Why not have the process for selecting, integrating, training and mentoring a new team member planned, documented and tested before it actually happens? Why wouldn’t you want the expectation that «this can happen» and «this is how we deal with it» in place and in front of the team and the client from the beginning?
 The longer a team works on a product, the more likely they are to develop «tunnel-vision.» They see the UI, but they become blind to the problems a new user might encounter trying to use it. They know there are newer technologies that might make something more efficient or resilient, but it takes time to test, advocate change, and demo the option to the client team. If what you have works, is it really worth the effort? The longer a team works together, the more «normal» the little quirks about a product become. In the long run, it can make them resistant to needed change and reluctant to suggest options.
The longer a team works on a product, the more likely they are to develop «tunnel-vision.» They see the UI, but they become blind to the problems a new user might encounter trying to use it. They know there are newer technologies that might make something more efficient or resilient, but it takes time to test, advocate change, and demo the option to the client team. If what you have works, is it really worth the effort? The longer a team works together, the more «normal» the little quirks about a product become. In the long run, it can make them resistant to needed change and reluctant to suggest options.- Working with the same people, on the same product, eventually leads to a level of isolation that can begin to make it difficult to want to get started on the «same old stuff» each day. Developers are part of «geek culture» and love to see new technologies, get input from other sources and try «cool» things. When this happens, production slips and members of the team may become less committed to the success of the product they are working on. It doesn’t happen in a day; it is a slow drip that eventually eats away at the team and makes it less effective. It can also make individuals on the team consider career changes because they are afraid their resume will reflect stagnation rather than stability.
- Bringing in «fresh (but experienced) blood» can bring cross-pollination from other experiences, new points of view on coding practices and processes, a new look at alternatives as you move forward and other benefits from another set of eyes on the project. If long term members of the project are not ready to accept new ideas, they can create strong resistance, but if they are positively primed for the idea by considering they could also benefit individually and as a team, it can be a shot in the arm for the team.
- «Ownership» of a product, or an area of responsibility, can be a strong motivator for a team. Their understanding of its deeper value and continued success is part of their pride and keeps the team on track. But, there is also a downside. If the team is the single point of knowledge and «truth» for a product, they are also the single point of failure. If there is no base of knowledge about the product outside of the team, in the wider pool of developers around them, there is no way to replace a team member easily or help them if there is a problem that causes a loss of a member or if the team runs into a serious internal disagreement (it does happen).
- Operationally, these long-term teams become silos. Outside the team, they are the go-to subject matter experts that always have the answers. Inside the team, individuals tend to become specialists, filling a niche that no one else can come close to. This not only runs against the whole concept of «agile organizations» – it becomes a growing risk within the organization.
There are more reasons too – but those concerns represent some of the more common drivers of the idea. They are all real issues and the problems the teams dealing with them have an impact on the projects they are in. But – does planned rotation actually solve the problems? Does the upside outweigh the downsides? Can rotation be planned well enough to overcome internal team dynamics? Will the supposed benefits last long enough to make rotations something you want to do? Can you actually present a case that would make client support, rather than oppose, the practice?
The answer would have to be – it all depends on implementation.
- Like any change, member rotations have to be sold internally before they can be implemented.
- Frank conversations about the health of teams, experiences in long term engagements have to be surfaced and alternative solutions have to be discussed.
- The timing and requirements for new members have to be considered and accepted by the existing team members. Simply dumping the idea on them without preparation is sure to bring disaster.
- The level of the incoming team member will make a difference in acceptance. Replacing a senior member with another senior developer may be more difficult than bringing in a mid-level or junior developer in their place. With less seniority, the new member will have lower expectations and less to live up to. They will be more accepting during knowledge transfer and mentoring and give existing team members new opportunities to grow. But if the outgoing member is considered to be a team leader, the impact may be very deep no matter who is brought in.
- If the practice is fairly new within the organization, replacing a team member is likely to be more problematic regardless of planning and thought. The practice can be new institutionally or within the team, it really doesn’t matter. If team members are not experienced with the concept, issues will arise. Assuming the issue will iron themselves out eventually is not a good way to manage change.
- Frequency is important. Single-member rotation will always cause thrash and lost productivity no matter how well it is planned. A team can only sustain so much change without becoming distracted and losing their center. In complex environments, it may take a considerable time for a new member to build up the necessary knowledge base. Most industry experience seems to circle around a period between six and nine months for the change of one member. More than that and the team might never gain cohesion again. Less than that and silos will begin to form. But, there is no perfect point. You can’t change a member during a critical release for a product, no matter what the calendar says. You have to work with the client team to gain acceptance and cooperation. Timing is a hard nut to crack and will be different in every situation.
This is an important and evolving area of management for outsourced agile teams. It is not widely discussed in the software development industry. Clients come to outsourcing vendors to avoid issues like team cohesion, resilience, and long-term stability. It may be difficult to bring them into a conversation about an issue that is seen as a vendor responsibility.
But, there are some ideas that are coming forward and worth considering. Larger outsourcing vendors can propose a dedicated «pool» rather than a team. The actual team in production continues to be a small number, but the vendor commits to a larger group, perhaps 7-10 including the active team, of developers that are involved and can become a team member with less overhead from change. This allows the members of the pool to become involved in project and product discussions, review code, and be the sounding board for ideas. There has to be an adjustment of the cost to allow this kind of an arrangement and a clear commitment by the vendor to avoiding the issues that are considered part of dedicated team contracts, but in certain situations, it is worth considering.
In the final analysis, it is hard to value the practice of rotating team members on dedicated teams. It can seem like a great idea if you have experienced the downsides of long-term engagements where unplanned changes and team stagnation become barriers to success. If the motivation, implementation, and outcomes are not carefully considered and monitored, it can become a serious distraction from productive development. Neither outcome is good so this is an important consideration and the decisions are likely to be different in every situation.
If you have experience with team member rotation (and not just fears or wild optimism) – I would be interested to hear your thoughts. This is still an unsettled area in agile team dynamics.
Scio is a provider of outsourced, dedicated and project teams for agile software development to our nearshore clients in North America. We have experience with many team and project configurations and would love to discuss how we could help with your next project. Please contact us with your questions.
Agile Methodology, Customer Experience, Nearshore, Product Development, Project Management, Successful Outsourcing
Work is always measured in some way. If you are doing repetitive work, the tendency is to measure the number of repetitions, like the pounds of fruit picked by a field worker in an hour or a day. If you are doing knowledge work, the tendency is to simply measure hours of work spent on the problem, assuming that a) the person doing the work has the necessary set of skills and a comprehensive knowledge base of the subject at hand and b) they spent enough time to evaluate the problem sufficiently and provide a balanced solution. If you are doing time and/or payment-dependent contract work, the main consideration is did you complete the work assigned in the contracted period and at the specified cost?
This all seems relatively benign and normal in the world of work because it assigns a value to work that can then be measured and evaluated in various ways. Did you pick more fruit this week than last? Did you solve more problems in this quarter? Did you complete all your contracted work on time and budget?
Software development is, of course, one of the most valuable types of knowledge work being done globally today. Since development is usually the domain of teams and is at this time, largely done with some form of agile and/or lean methodologies, the measurements tend to be a combination of individual and team metrics applied by various means. Some common metrics are:
When we get beyond these three common methods and their minor variations, we start getting into more complex models (!!) that tie team performance, quality, project length, man-hours, adherence to production and methodology standards and complex team models in DevOps implementations.
We Have Questions
At the end of the exercise, however, it is done, we end up with some sort of measurement of the work of software development. But as we do, we need to ask ourselves a few important questions:
 What does our measurement tell us? What is it not telling us? If we are measuring lines of code or functions, is the measurement telling us if the work was efficient or just an output meant to produce more (or a given number of) lines/functions over a given period? Were the lines of code or functions really efficient and useful? Programming is very comparable to writing. Some writers are more efficient at expressing thought and others see a more elegant way to express a thought without addressing it directly. Some programmers are more efficient because they reuse code multiple times throughout the source with efficient use of variables. Some functions in a program are critical and getting them right is tough, requiring time and effort. Other functions are simply «eye-wash» and don’t have a real bottom-line value. There as many ways to game the system as there are ways to produce better code with fewer lines. Every programmer, every team, and every project has different dynamics depending on the language being used, the type of environment, the technical problem being dealt with and many other factors. If you use a pure «number of X metric,» you have to be clear about what it means and doesn’t address.
What does our measurement tell us? What is it not telling us? If we are measuring lines of code or functions, is the measurement telling us if the work was efficient or just an output meant to produce more (or a given number of) lines/functions over a given period? Were the lines of code or functions really efficient and useful? Programming is very comparable to writing. Some writers are more efficient at expressing thought and others see a more elegant way to express a thought without addressing it directly. Some programmers are more efficient because they reuse code multiple times throughout the source with efficient use of variables. Some functions in a program are critical and getting them right is tough, requiring time and effort. Other functions are simply «eye-wash» and don’t have a real bottom-line value. There as many ways to game the system as there are ways to produce better code with fewer lines. Every programmer, every team, and every project has different dynamics depending on the language being used, the type of environment, the technical problem being dealt with and many other factors. If you use a pure «number of X metric,» you have to be clear about what it means and doesn’t address.- Is our measurement comparable? Can it be used over the long term or compared across projects or teams? Frequently, this is where the complex math becomes part of the equation and frankly, begins to fail to do its job effectively. The more we try to «normalize» measurements across a single project, between teams, and across projects and teams, the more subjective the outcome becomes. Were the technical hurdles encountered at the beginning of Project A really comparable to Project B? If we decide there is a significant difference, how do we adjust for it? Did Team A experience more changes in team composition than Team B? How do we account for that issue? Are we comparing skill levels, experience, time to reach «normal productivity» or some other factor? Was Team A really suited to provide the skills and experience needed for the given project? Did their productivity fail to reach the levels expected because of issues outside of their control? In most cases, the more you try to normalize between measures of productivity between individuals, teams, and projects, the less sure you can be you have a reasonable common measure. And in the end, the question becomes, is a comparable metric what we really need?
 Isn’t any measurement better than no measurement? Can we afford to fly blind? Certainly, if you have an outsourced team, multiple teams, and/or multiple projects you have to begin to understand why some projects seem to work well and some don’t. You need to be able to judge if a project is going off the tracks so you can get it back in line before the problem becomes critical. Finding ways to measure performance and productivity would seem to be the best tool to address the common issues in software development projects. But if the measurements we are using aren’t really addressing the problems we have, how are they helping us? Are they really more than just busy work for managers and bean counters?
Isn’t any measurement better than no measurement? Can we afford to fly blind? Certainly, if you have an outsourced team, multiple teams, and/or multiple projects you have to begin to understand why some projects seem to work well and some don’t. You need to be able to judge if a project is going off the tracks so you can get it back in line before the problem becomes critical. Finding ways to measure performance and productivity would seem to be the best tool to address the common issues in software development projects. But if the measurements we are using aren’t really addressing the problems we have, how are they helping us? Are they really more than just busy work for managers and bean counters?
The more we look at the problem, the more we begin to understand that measurement for the sake of monitoring «something» isn’t really useful. But on the other hand, measuring any aspect of software development is better than monitoring nothing at all and simply hoping everything will work out in the end. Even a weak measurement provides some level of confidence if it is used consistently and we understand its shortcomings well enough.
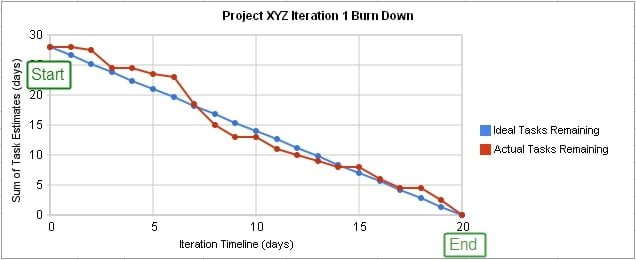
In agile teams, there is another, more important way to look at things. If we give the team simple methods they agree on and understand, like story points and burn down charts, they will know when they are performing well and when they are pushing too large a boulder up a hill. Inside the team, they know who is consistently performing and producing efficient code with fewer problems. The team knows when its backlog is too great to finish in the allotted time. Team members learn quickly who can be asked for pointers on how to approach a problem properly and who cannot be depended on reliably. We can stand around, pointing out issues with the common ways to measure agile team performance, but their value is those common agile methods are basically useful to the team to understand where they stand in relation to the work ahead of them and their quality performance. Where we get into trouble is when we try to extract the common measures and try to draw larger conclusions from them.
The Reality is – Communication is the Key
If we get past trying to use performance metrics outside of a single project and narrow our focus to what they do for a team inside of a project, we begin to see their value more clearly. The team knows what is going on. They may attempt to fool themselves or others, but in the end, they can see the light in the tunnel and they know if it is a successful end to the project or an approaching train. The problem is to get them to trust each other and the larger team enough to surface the problems they see as soon as they see them, without fear.
The level of trust and responsibility required for open communication and collaboration is perhaps the largest problem faced in software development projects. It is the «why» behind the invention and popularity of the agile and lean methodologies in wide use today. Conversely, the larger the organization, the more critical and costly the project is to the organization, the less likely it is that the team will feel and be enabled to inquire and speak out about the problems they believe they are facing. In a large organization, metrics are the shorthand to avoid having «high touch» with every team and individual. In a costly, critical project, metrics are meant to be the «truth-tellers» to assure stakeholders that things are well controlled, even though everyone knows that metrics can be gamed without much problem. And the more the metrics are relied on, instead of the knowledge inside of the team, the more likely it is the project will get out of hand before the problems are addressed.
Responsibility. Trust. Communication.
So what is the bottom line on measuring performance and productivity in software development projects?
- Measurement is most useful inside the software development team itself,

Planning Poker
where the knowledge resides about what is really going on from day today. Everywhere else, it is just as likely to be smoke and mirrors as it is, to be honest, and useful – depending on who is using the metrics and for what purpose. If the team doesn’t understand the metrics applied and can’t use them to better understand where they are in relation to the work to be done, their quality performance and general efficiency as a team, the metrics will fail to give back their primary value – keeping the team and project on track.
-
The agile methodology relies on individual and team responsibility, trust and communication. If these three points cannot be achieved within a team, agile and scrum are just a bunch of processes and procedures that may or may not be helpful in organizing work. If the team is just «going through the motions» in taking responsibility for tasks, assessing and managing their backlog, and participating in standups and retrospectives, additional metrics and measurement will not provide much value. They will provide information to a larger audience too late to enable outside forces to do more than triage injuries to the project.
- Working through what may appear to be problems or what may seem to be a simple solution requires peer-level coaching and communication, not blame. If we understand that the team itself really knows what is going on – getting them to assess the problem honestly and figure out how to address it requires something other than pointing fingers, avoiding issues and top-down communication. It also means that the team needs to take responsibility, as soon as anyone recognizes a problem could be on the horizon, to consider it seriously and determine both the size of the problem and solutions that could be used to address it. And so what if the team raises an issue that may turn out to be nothing of great importance? We’ve been called to action to look at it and we will all come out of the conversation wiser. If everyone in the conversation addresses each other as a peer, rather than hierarchically, there is a good reason to think that the next time a problem is encountered or perceived, it will be openly addressed, rather than swept under the rug.
Three points to consider and use in conjunction with standard agile and scrum-based tools. You can use more and you can draw all sorts of conclusions from the systems you bring together. But in the end, if they don’t bring immediate value back to a current project, what value are they really serving?
Looking for a development team? Contact us we can help you!
Scio provides nearshore software development services for our client base in North America. We work closely with our clients to ensure that the projects we are involved in have the level of communication and understanding needed to reach successful outcomes. If you have a project where you think we could help, please contact us. We would be happy to discuss your needs.
Agile Methodology, Customer Experience, Nearshore, Product Development
Common Myths & Misconceptions for Distributed Agile Teams in Software Development
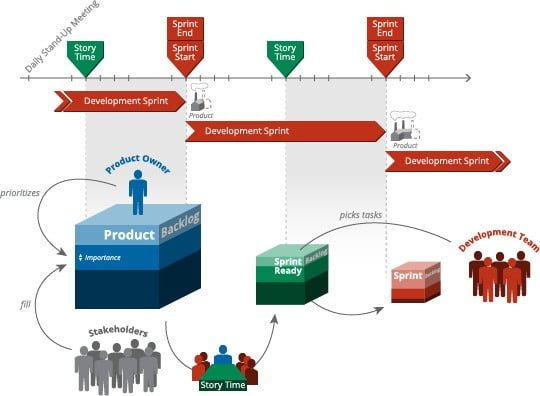
Throughout this series, we have explored some of the best practices for agile-scrum teams, but in the light of distributed team situations. Scio provides software development teams – working from our development center in Morelia – for projects throughout North America. Our practices, methodologies, and culture are tuned to distributed team situations in a nearshore deployment. We discuss the realities of outsourcing and distributed teams with our prospects and clients on a regular basis. As we wrap up this series, let’s discuss some of the common myths and misconceptions that we hear about frequently.
There is no additional overhead for projects using distributed teams for agile-scrum projects.
Reality: Shared vision, communication, strong procedures, and planning are part of the required overhead for working smart in a distributed team environment. But, the truth is – these same elements should be part of any software development project to ensure success. While a distributed environment requires more rigor and attention to details, all projects benefit from addressing these issues.
More specification must be done at the start of a distributed team project
Reality: Increasing the upfront development of specifications for an agile-scrum project creates a false sense of security and understanding. When something needs to change, there will be latent resistance. There is an increased focus for the full team on understanding where the team(s) are and assuring knowledge is shared – but that should be a normal part of communication in any situation.
Distributed teams cannot do agile and scrum
Reality: If teams are able to organize independently, are cross-functional, collaborative, etc. – there is an overhead in coordination between teams (scrum of scrums) but mitigation in the form of improved awareness of the state of tasks can keep it to a minimum. It is much better to spend resources on coordination than fixes because one team went off the track, wasting time and resources.
Distributed teams have lower quality, more redo’s
Reality: If teams are cross-functional, managing their own tasks and backlog, enabled to work directly with the product owners, have a full development environment using test-driven development, continuous integration and practice regular builds on the central repository for the project, a great number of problems can be avoided. Regular team-wide meetings for planning, pruning, technical issues are overhead, but they will lower impediments greatly if done with openness and trust.
In larger projects, it is better to work as one team than two or more smaller teams even if some members are not co-located with the majority of team members
Reality: The communication and planning overhead does not go down in one larger team in comparison to two or more smaller teams, it rises. Size matters – smaller, self-organizing teams are more efficient overall. Team members in a larger team have less push to be individually responsible and to participate actively in the project. They can easily «hide» in the larger team. In larger teams, the overhead for work review actually climbs, because of the number of people who have to be informed and communicated with. And if the «larger team» is composed of remote members without properly recognizing them as distributed teams or single outside team members – the adherence to standard methodology, processes and assurance procedures tends to drop dramatically. They are literally «out of sight, out of mind.»
There are a lot more things that could be said, but the bottom line is – best practices matter in all agile-scrum projects. Agile is not a license to operate without structure – quite the opposite. It depends on individual responsibility, communication, and adherence to the processes and methodologies adopted by the project team. Agile is adaptive. It will scale along with scrum to situations with distributed teams. Teams that adopt the practices and procedures necessary to be successful in distributed situations as a part of their regular work patterns will have better results in all situations.
We hope this series has been useful and informative for you – helping you to understand what is «behind the curtain» in successful projects and some of the lessons we have learned in the field. If you have a project that you believe could benefit from a team that understands how to leverage agile and scrum in a nearshore implementation, don’t hesitate to contact us.

Agile Methodology, Customer Experience, Nearshore, Project Management
Organizational & Team Best Practices
In the previous article in this series, we started exploring the general organizational and team best practices for agile-scrum projects. In this article, we’re going to finish up a few basic issues and then move into points for distributed teams specifically.
As we have said, the main issue to be considered for software development with agile-scrum teams is communication. If communication is in any way blocked or stifled by cultural or organizational constraints, the team and the project will suffer. In a very real way, knowing how far along the work is on a given user story is part of that communication. We discussed building the technical elements of a system for test-driven development and continuous integration for projects, but there is an organizational element too. Team members must feel these tools are a part of their obligation to their team. They must use them religiously and fully to ensure the tools are doing the job of maintaining code and the development process for all team members. Here a few simple rules to live by:
- All development team members should check work into the common code base as frequently as possible.
- Automated, continuous builds should be run hourly with full logs turned on.
- Each individual team member must exchange a clean build by the end of their shift. Avoid situations where an individual is allowed to push multiple builds outside team core hours that could take planned work or tasks off course.
- If a specific development issue is to be addressed outside of core hours by developers, ensure the scope, limitations, and boundaries are clearly negotiated with everyone and adhered to.
Distributed Team Best Practices

When a software development project is based on distributed teams, some specific organizational practices need to be considered. It isn’t enough to just set up groups in a couple of places, and expect everything to work like it did when you were all sitting in the same big room and able to just turn around and see your teammate.
The first point to consider is how each distributed team in the project will work. One common practice is to put all the QA (as an example) in one team and to have another team be just developers. The problem is – when locations are role-based, they tend to lose overall team collaboration and become an island to themselves. The tendency in this situation is to move to an «us against them» mentality. To avoid this, set up fully cross-functional teams that have their own user stories and backlog. It promotes the team and individual responsibility and gives them a clear role in the project as a whole.
With that in mind, there are a few additional points to consider:
- Use feature-based, rather than component or layer-based teams because it ensures teams continue to have a feeling of being integrated with other teams with shared vision and knowledge. It also allows them to be more flexible if the project changes. They can take on a different backlog because they understand where the project is going.
 Distribute work evenly – don’t allow one team to sit fallow while another catches up. This, of course, implies that regular discussions of workload (a scrum of scrums), dependencies, and assumptions is critical to the balance on the project as a whole.
Distribute work evenly – don’t allow one team to sit fallow while another catches up. This, of course, implies that regular discussions of workload (a scrum of scrums), dependencies, and assumptions is critical to the balance on the project as a whole.- When a team has a local «proxy» for the client-side product owner, it is critical that that proxy role has daily contact and communication with the core product owner to assure they can make decisions quickly and with the assurance they are in sync with the current vision.
- Each team must feel enabled to clarify issues directly with the client side (they have their own user stories – remember…) and not be tied to a chain of notification. Invariably, notification chains shorten messages, misunderstand the context, and create communication loops that just slow down clarification and decisions.
- Teams must have daily points of contact between them (scrum of scrums again) to discuss progress, dependencies, impediments, etc. and assure product owners are not being quarried about the same issues multiple times.
One Team Member «Outside»
There are times when it is necessary to have one lone team member outside the main development group or even a couple of individuals remotely located by themselves. This is not an unusual situation, but it is one that takes care to handle properly. All the work you do to assure a cohesive, collaborative team can be lost when one remote member is not paying their role and participating in the process properly.
In basic terms, all the distributed team and organizational best practices apply except:
- Single development team members cannot be a stand-alone unit in the same way a minimal team can – so they need to be formally paired with other team members in a way that assures they will remain «in the loop» throughout the project. To make this work, consider pair programming (especially early in the project) and pairing with a specific QA.
- Avoid situations where single team members are outside of the team core hours more by more than one or two hours. Longer isolation will simply assure they will not integrate easily with the rest of the team – they will remain the lone wolf on the outside you have to watch constantly to assure they don’t go off course.
- «Standard practices» (development environment, burndown chart, shared repositories, active participation in meetings, communication systems, etc. become critical resources to assure the remote team member feels they are a fully integrated and vital part of the project. All aspects of processes must be proven, clearly documented and relatively easy to setup and use.
- If the remote team member is new to your procedures and processes, have a standard initiation program as a part of the project initiation or before. The program should include not just the setup, practices and methodologies necessary to understand the way the team will operate. It should also include the reasoning and expectations they as a team member will operate under.
The single team member working remotely deserves some special consideration. They must feel they are part of the organization and able to be productive in their environment. For that reason, it is important to consider if they are working from their home, what kind of set up they have. Do they have good networking? Do they have a regular work area with good ventilation, light, and isolation from distractions? A worker at home, with the TV blaring in the other room or perhaps a baby that requires attention on a regular basis is going to find it very difficult to be as productive as their teammates. What can you do to assure they are not at a disadvantage? Consider issues in the same way you would any impediment in agile development – what can you do to move the impediment out of their way?
The Take-Away
In the end, it should be easy to see that that making an agile-scrum project successful with distributed teams is nothing more than doubling down on the best practices that are an integral part of agile. If they were important in a team in a single location, they are doubly important in a distributed team and have even more impact on project outcomes. Does a distributed team model immediately burden a project with additional overhead? Well, we will discuss this aspect more in the last article in this series, but the simple answer is no. If you have been using best practices for agile-scrum projects religiously – a project with distributed teams just requires a little more focus and diligence. If you were not as judicious as you should be about your practices, then yes, there will be overhead because your risk of failure will be much higher for distributed teams until you get your practices in line.
In our last article in this series, we will explore common myths that crop up whenever anyone proposes any level of distributed teams in software development. Remember, as a nearshore software development provider, these are objections we discuss with potential clients regularly. So join us – won’t you?
If you jumped into the middle of this series, you can go back to the start here.

Agile Methodology, Customer Experience, Nearshore, Product Development, Project Management
Organizational and Team Best Practices
While it might seem that adopting the agile-scrum framework to distributed teams is all about the right tools (especially if you read marketing materials from tool makers), in general, it is more about how you organize your teams and processes than anything else. For that reason, we decided to break this part of the discussion into two sections. Our assumption is you are only going to read so much during your breaks between meetings, on your smartphone….
Project Initiation
 There are all sorts of reasons that a «kick-off» meeting is critical for project success, in fact, we’ve already talked about a few in the earlier posts from this series. But in this part of the series, we’re focusing on the organizational elements of a successful agile-scrum software development team.
There are all sorts of reasons that a «kick-off» meeting is critical for project success, in fact, we’ve already talked about a few in the earlier posts from this series. But in this part of the series, we’re focusing on the organizational elements of a successful agile-scrum software development team.
One of the areas that are especially important is the cohesion and understanding between the individual members of the team. If it is not taken care of the upfront, it can take a long time to build. If you are not aware of the teaming model developed by Bruce Tuckman, this is a good time to start considering it. In short, Mr. Tuckman found that teams follow a regular pattern of «storming, norming and performing» during their lifecycle. If you can shorten this cycle and get too strong performance sooner, you are better off. We have found that kickoffs that include games, team-building, and participative events go a long way to achieving this goal. In fact, for longer projects, planning similar events around specific milestones prevents teams from going back through the cycle later in the process.
There are many guides available for these activities, but regardless of which ones you find useful, the actual activities are not something you can simply jump into and do from a book. It takes practice and experience to successfully integrate team activities into project initiation so the sooner you start using them the better. We have found teaming model to be an excellent resource, but again, it requires some hands-on experience to use successfully.
What do you need to do to assure success for project initiation meetings?
- Include as many team members as possible in a single location, even if some must travel greater distances. The time and expense will pay off handsomely in the end.
- If some team members or teams cannot attend, arrange parallel events that the teams can report on or share in an online conference format (voice, video, photos, etc.).
- Sync your agile – scrum processes, artifacts, and ceremonies across teams and participants with actual sessions during the joint event. Execute sprints if possible (use Sprint 0 as a base). Set expectations with everyone that the processes will be standardized and adhered to across the entire team.
- Establish a shared product vision with presentations, question/answer sessions, product games, etc.
- Agree on core project hours for the entire team (including product owners, proxies, etc.) and communication standards. Core hours should overlap considering the time zones involved. Ensure everyone commits to core hours and provides proxies if they cannot be reached.
- Agree to set regular meetings during core hours even if not everyone expects to be in the meetings. This assures if questions come up during the meetings, they can be quickly answered.
- Agree on timing for sprint planning, retrospectives, and other planning activities. The more standardized the timing for these meetings, the more likely they will be to be integrated into individual routines.
- Learn and respect cultural viewpoints across the team, festivals, language preferences. Plan to share status around holidays, common activities, etc.
- Encourage an atmosphere of fun, respect, and collaboration.
This is a lot to accomplish in any timeframe, much less a day or a few hours. Project kickoffs must be carefully planned and managed. They could and often should take more than a day. We’ve had initial meetings, including initial work, take as long as a week. Once you have dealt with them to and from aspects of the travel, the rest is relatively inexpensive – so don’t push to shorten the time more than necessary.
Best Practices for All Scenarios

Planning component breakdown during the kickoff.
We’ve said that part of making agile-scrum for distributed teams successful is including many of the necessary best practices in all projects, not just the ones with distributed members. These best practices are critical for distributed teams, but also just good practice in any software development project. Your distributed teams will «catch on» quicker if these are part of your regular practice and adapt to new situations better.
- Participation by every individual in the team in meetings is always important. That said, it isn’t natural for everyone. Team members must be positively coached to engage in active, personal participation. Avoiding situations where one person becomes the de facto spokesman for the team helps to ensure team members don’t sit back and not contribute. Trust is an important element in participation. Team members must feel comfortable questioning ideas and playing devil’s advocate when necessary to draw out concepts and beliefs. Each team member must feel enabled to speak directly with the client/project team to avoid forming communication chains that will inevitably muddle and shorten their message.
- Plan frequent live demos and retrospectives with time for questions and clarifications. Communication in these meetings should not be more tightly time-bound than necessary, but when long conversations do surface, don’t be shy about moving them to a parking lot to be addressed in a specific meeting meant to resolve that issue with the right people involved.
- Scrum masters should be careful to practice servant-leadership roles. They need to concentrate on removing impediments so tasks can move forward rather than prescribing how tasks should be done.
- Pre-plan a larger window of future sprints on a weekly basis (depends on the length of sprints) specifically to expose interdependencies between teams, roles, etc. and groom backlogs with the team as a whole.
- Lean to short sprints rather than long and synchronize/prioritize between teams regularly. Avoid situations where a team could go too far down a path before syncing with others.
- Have irregular, casual «brown-bag» sessions to discuss technical alignment, decisions and common ground among members and teams.
- Find ways to rotate team members. Rotation can be between locations, roles, among teams, etc. Don’t allow individuals to become insular units by themselves or with specific team members. Accomplishing this goal can be challenging, but it is especially important in longer projects. Rotation should not be «one way» (always to the client site for instance) and where it isn’t possible, consider remote pairing too as an alternative.
Granted, these points are not easy to accomplish. They take planning and practice to get right – but the aim is to ensure a successful project and enough cannot be said about how much of success is preparation. The next installment in this series will continue to explore organizational and team issues, there is a lot to cover. We will also cover issues related to specific scenarios that we have found take a slightly different approach. I hope you will stay with us to see how important it is to understand software development projects in an agile-scrum environment and learn more about what is needed to extend it to distributed teams.
If you are coming in the middle and want to jump back to the start of the series, you can start here. Or if you are looking for a software development partner and want to contact us, just click here and leave us a message and we will be contacting you ASAP.

 The longer a team works on a product, the more likely they are to develop «tunnel-vision.» They see the UI, but they become blind to the problems a new user might encounter trying to use it. They know there are newer technologies that might make something more efficient or resilient, but it takes time to test, advocate change, and demo the option to the client team. If what you have works, is it really worth the effort? The longer a team works together, the more «normal» the little quirks about a product become. In the long run, it can make them resistant to needed change and reluctant to suggest options.
The longer a team works on a product, the more likely they are to develop «tunnel-vision.» They see the UI, but they become blind to the problems a new user might encounter trying to use it. They know there are newer technologies that might make something more efficient or resilient, but it takes time to test, advocate change, and demo the option to the client team. If what you have works, is it really worth the effort? The longer a team works together, the more «normal» the little quirks about a product become. In the long run, it can make them resistant to needed change and reluctant to suggest options.

 What does our measurement tell us? What is it not telling us? If we are measuring lines of code or functions, is the measurement telling us if the work was efficient or just an output meant to produce more (or a given number of) lines/functions over a given period? Were the lines of code or functions really efficient and useful? Programming is very comparable to writing. Some writers are more efficient at expressing thought and others see a more elegant way to express a thought without addressing it directly. Some programmers are more efficient because they reuse code multiple times throughout the source with efficient use of variables. Some functions in a program are critical and getting them right is tough, requiring time and effort. Other functions are simply «eye-wash» and don’t have a real bottom-line value. There as many ways to game the system as there are ways to produce better code with fewer lines. Every programmer, every team, and every project has different dynamics depending on the language being used, the type of environment, the technical problem being dealt with and many other factors. If you use a pure «number of X metric,» you have to be clear about what it means and doesn’t address.
What does our measurement tell us? What is it not telling us? If we are measuring lines of code or functions, is the measurement telling us if the work was efficient or just an output meant to produce more (or a given number of) lines/functions over a given period? Were the lines of code or functions really efficient and useful? Programming is very comparable to writing. Some writers are more efficient at expressing thought and others see a more elegant way to express a thought without addressing it directly. Some programmers are more efficient because they reuse code multiple times throughout the source with efficient use of variables. Some functions in a program are critical and getting them right is tough, requiring time and effort. Other functions are simply «eye-wash» and don’t have a real bottom-line value. There as many ways to game the system as there are ways to produce better code with fewer lines. Every programmer, every team, and every project has different dynamics depending on the language being used, the type of environment, the technical problem being dealt with and many other factors. If you use a pure «number of X metric,» you have to be clear about what it means and doesn’t address.




 Distribute work evenly – don’t allow one team to sit fallow while another catches up. This, of course, implies that regular discussions of workload (a scrum of scrums), dependencies, and assumptions is critical to the balance on the project as a whole.
Distribute work evenly – don’t allow one team to sit fallow while another catches up. This, of course, implies that regular discussions of workload (a scrum of scrums), dependencies, and assumptions is critical to the balance on the project as a whole.
 There are all sorts of reasons that a «kick-off» meeting is critical for project success, in fact, we’ve already talked about a few in the earlier posts from this series. But in this part of the series, we’re focusing on the organizational elements of a successful agile-scrum software development team.
There are all sorts of reasons that a «kick-off» meeting is critical for project success, in fact, we’ve already talked about a few in the earlier posts from this series. But in this part of the series, we’re focusing on the organizational elements of a successful agile-scrum software development team.